LED Bulb Manufacturing Cost Analysis: Bright Ideas, Better Costs

What is LED Bulb?
An LED bulb is a solid-state lighting device that uses Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) as its illumination source. Different from incandescent or fluorescent lamps, light in LED bulbs is produced by electroluminescence, a process where the passing of an electric current through a semiconductor material emits photons directly. This process is highly energy-efficient, with a far larger percentage of the electricity being converted to usable light and very little heat generated in the process. LEDs are designed with components like drivers, heat sinks, lenses, and diffusers, among others, that control their brightness, color, and thermal performance. With long life, low power consumption, and durability, they become one of the most sought-after lighting technologies for residential, commercial, industrial, and outdoor applications.
Key Applications Across Industries:
LED bulbs are widely used in residential, commercial, industrial, automotive, and public infrastructural applications due to their adaptability, energy efficiency, and long operational life. In homes, LED bulbs replace traditional lighting in rooms, kitchens, outdoor areas, and decorative fixtures, offering options such as warm white, cool white, multicolor RGB, and smart dimmable variants. Their compatibility with smart-home ecosystems allows integration with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and voice-controlled systems, making them central to modern home automation.
LED light bulbs offer consistent lighting for productivity and ambiance, with economic benefits from reduced energy bills in commercial office spaces, retail stores, hospitals, hotels, and educational facilities. Their support of tunable white or human-centric lighting systems helps improve occupant comfort.
In industrial settings, LED bulbs find their applications in warehouses, factories, and areas of production because high-lumen output, shock resistance, and long service intervals reduce maintenance downtime. LEDs also play an important role in street lighting, parking lots, airports, and transportation junctions since they improve visibility and safety while reducing operational costs.
Specialty uses include automotive lighting-turn signals, headlamps, and interior lights; agricultural controlled-environment farming applications; and architectural lighting, with an emphasis on design. LEDs also support emergency lighting, signage, and display systems. Their versatility spans energy-efficient retrofits through cutting-edge smart-lighting systems: they are one of the most widely used forms of lighting globally.
What the Expert Says: Market Overview & Growth Drivers
The global LED bulb market reached a value of USD 10.2 Billion in 2024. According to IMARC Group, the market is projected to reach USD 24.0 Billion by 2033, at a projected CAGR of 9.85% during 2025-2033. The global LED bulb market is growing rapidly because of the increasing demand for energy-efficient lighting, government regulations favoring low-consumption products, technological advancements, and ongoing replacement of outdated lighting systems. Among the influential factors are a global trend towards sustainability wherein many countries have phased out incandescent and halogen lamps while promoting LEDs by using incentives, subsidies, or efficiency standards. With rising electricity costs and strengthening climate policies, consumers and commercial users alike increasingly adopt LED solutions to cut down on power consumption and lower carbon footprints.
Another major driver is the growth of urbanization and infrastructure development, accelerating demand for LED lighting in residential housing, commercial buildings, smart cities, and public lighting projects. LEDs offer high lumen output, long lifespans, and reduced maintenance-all positive attributes pertinent to large-scale deployments such as roadways, railways, airports, and industrial parks.
Features enhancing market adoption include smart lighting, integration into IoT, color-tunable LEDs, Li-Fi technology, and better thermal management. Above all, smart LED bulbs attract tech-savvy consumers who seek automation, remote control, and energy monitoring.
LEDs also enable various emerging trends in human-centric lighting, offering changeable color temperatures that improve mood, productivity, and well-being. They also play a significant role in commercial retrofitting; especially as older buildings are renovated to meet today's energy standards.
Declining manufacturing costs and improvements in semiconductor efficiency continue to make LED bulbs more affordable. This, in addition to growing e-commerce, means product availability is widespread, which also pushes adoption in rural and developing areas. Overall, sustainability goals, infrastructure growth, evolving lighting technologies, and cost savings together fuel robust global demand for LED bulbs.
Case Study on Cost Model of LED Bulb Manufacturing Plant:
Objective
One of our clients reached out to us to conduct a feasibility study for setting up a medium scale LED bulb manufacturing plant.
IMARC Approach: Comprehensive Financial Feasibility
We developed a comprehensive financial model for the setup and operation of a proposed LED bulb manufacturing plant in India. This plant is designed to manufacture 2 million units of LED bulb annually.
Manufacturing Process: The production of an LED bulb requires several steps in semiconductor fabrication, electronic assembly, optical design, and quality testing to ensure efficiency, durability, and safe illumination. Manufacturing typically starts by creating the chip of the LED, usually from GaN grown on substrates such as sapphire or silicon carbide using epitaxy growth methods like MOCVD. Light-emitting layers are formed by growing a wafer of semiconducting material, after which chips are separated, mounted onto lead frames or ceramic packages, and wire-bonded. The packaged LED is then coated with phosphor materials in order to achieve desired color temperatures and convert blue or UV light into warm or cool white light. Next, the LED packages are integrated onto a printed circuit board using surface mount technology. It contains a driver circuit for converting AC mains power into regulated DC current suitable for LEDs. High-quality drivers include components for rectification, current regulation, surge protection, and flicker reduction. Thermal management is critical, so the assembly is attached to a heat sink made from aluminum in order to dissipate heat and maintain long diode life. An optical assembly is added, including lenses, diffusers, or reflectors, to control the light output, distribution, and glare. These optical parts are usually injection-molded from polycarbonate or acrylic. All components are then enclosed within the bulb housing, which may be made of plastic, glass, aluminum, or composite materials. It undergoes comprehensive testing for luminous flux, color accuracy, thermal stability, power factor, electrical safety, and life-cycle performance after assembly. The packaging and labeling come next, after which each of the bulbs will have met regulatory and quality standards to reach either consumer, commercial, or industrial markets.
Get a Tailored Feasibility Report for Your Project Request Sample
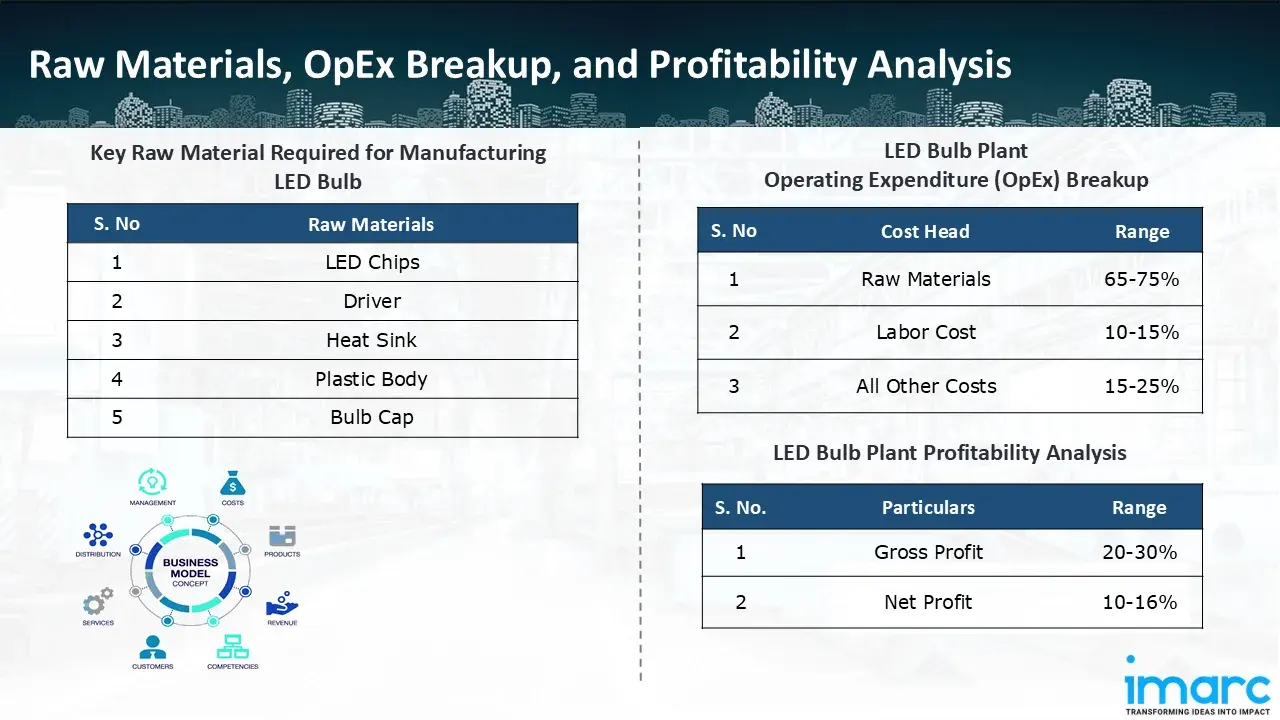
Raw Material Required:
The basic raw materials required for LED bulb manufacturing include:
- LED Chips
- Driver
- Heat Sink
- Plastic Body
- Bulb Cap
Machine Section or Lines Required:
- SMT Line
- Assembly
- Aging
- Testing
Techno-Commercial Parameter:
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): Capital expenditure (CapEx) in a manufacturing plant includes various investments essential for its setup and long-term operations. It covers machinery and equipment costs, including procurement, installation, and commissioning. Civil works expenses involve land development, factory construction, and infrastructure setup. Utilities such as power, water supply, and HVAC systems are also significant. Additionally, material handling systems, automation, environmental compliance, and safety measures are key components. Other expenditures include IT infrastructure, security systems, and office essentials, ensuring operational efficiency and business growth.
- Operating Expenditure (OpEx): Operating expenditure is the cost incurred to operate a manufacturing plant effectively. Opex in a manufacturing plant typically includes the cost of raw materials, utilities, depreciation, taxes, packing cost, transportation cost, and repairs and maintenance. The operating expenses are part of the cost structure of a manufacturing plant and have a significant effect on profitability and efficiency. Effective control of these costs is necessary for maintaining competitiveness and growth. Furthermore, raw material cost in LED bulb manufacturing plant ranges between 65-75%, labor cost ranges between 10% to 15%, and all other costs ranges between 15-25% in the proposed plant.
- Profitability Analysis Year on Year Basis: We assisted our client in developing a detailed cost model, which projects steady growth, with revenue rising throughout the projected period. Moreover, gross profit margins lie between a range of 20-30%, and net profit lie between the range of 10-16% during the income projection years, highlighting strong financial viability and profitability.
Conclusion & IMARC's Impact:
Our financial model for the LED bulb manufacturing plant was meticulously developed to meet the client’s objectives, providing an in-depth analysis of production costs, including raw materials, manufacturing, capital expenditure, and operational expenses. By addressing the specific requirements of manufacturing 2 million units of LED bulb annually, we successfully identified key cost drivers and projected profitability, considering market trends, inflation, and potential fluctuations in raw material prices. This comprehensive financial model equipped the client with valuable insights into strategic decision-making, demonstrating our commitment to delivering high-quality, client-focused solutions that ensure the long-term success of large-scale manufacturing ventures.
Latest News and Developments:
- In November 2025, Yeelight, a leading global manufacturer of smart lighting solutions, today announced the debut of its latest innovation – an 11W RGBCW smart bulb providing an amazing 1300 lumens. The newly released Yeelight smart bulb offers unrivalled adaptability with five-channel dimming (Red, Green, Blue, Cold White, Warm White) and better energy efficiency.
- In May 2025, a joint venture between Krut LED LLC and Havells International, a fully owned subsidiary of Havells India Limited, Havells Lighting LLC has formally begun operations to cater to the American lighting market.
- In March 2025, Uno Minda introduces Premium Ultimo Pro+ LED Lighting Bulb Range for 2-Wheelers in the Indian aftermarket.
Why Choose IMARC?
IMARC's Financial Model Expertise: Helping Our Clients Explore Industry Economics
IMARC is a global market research company that offers a wide range of services, including market entry and expansion, market entry and opportunity assessment, competitive intelligence and benchmarking, procurement research, pricing and cost research, regulatory approvals and licensing, factory setup, factory auditing, company incorporation, incubation services, recruitment services, and marketing and sales.
Under our factory setup services, we assist our clients in exploring the feasibility of their plants by providing comprehensive financial modeling. Additionally, we offer end-to-end consultation for setting up a plant in India or abroad. Our financial modeling includes an analysis of capital expenditure (CapEx) required to establish the manufacturing facility, covering costs such as land acquisition, building infrastructure, purchasing high-tech production equipment, and installation. Furthermore, the layout and design of the factory significantly influence operational efficiency, energy consumption, and labor productivity, all of which impact long-term operational expenditure (OpEx). So, every parameter is covered in the analysis.
At IMARC, we leverage our comprehensive market research expertise to support companies in every aspect of their business journey, from market entry and expansion to operational efficiency and innovation. By integrating our factory setup services with our deep knowledge of industry dynamics, we empower our clients to not only establish manufacturing facilities but also strategically position themselves in highly competitive markets. Our financial modeling and end-to-end consultation services ensure that clients can explore the feasibility of their plant setups while also gaining insights into competitors' strategies, technological advancements, and regulatory landscapes. This holistic approach enables our clients to make informed decisions, optimize their operations, and align with sustainable practices, ultimately driving long-term success and growth.
Our Clients
Contact Us
Have a question or need assistance?
Please complete the form with your inquiry or reach out to us at
Phone Number
+91-120-433-0800+1-201-971-6302
+44-753-714-6104